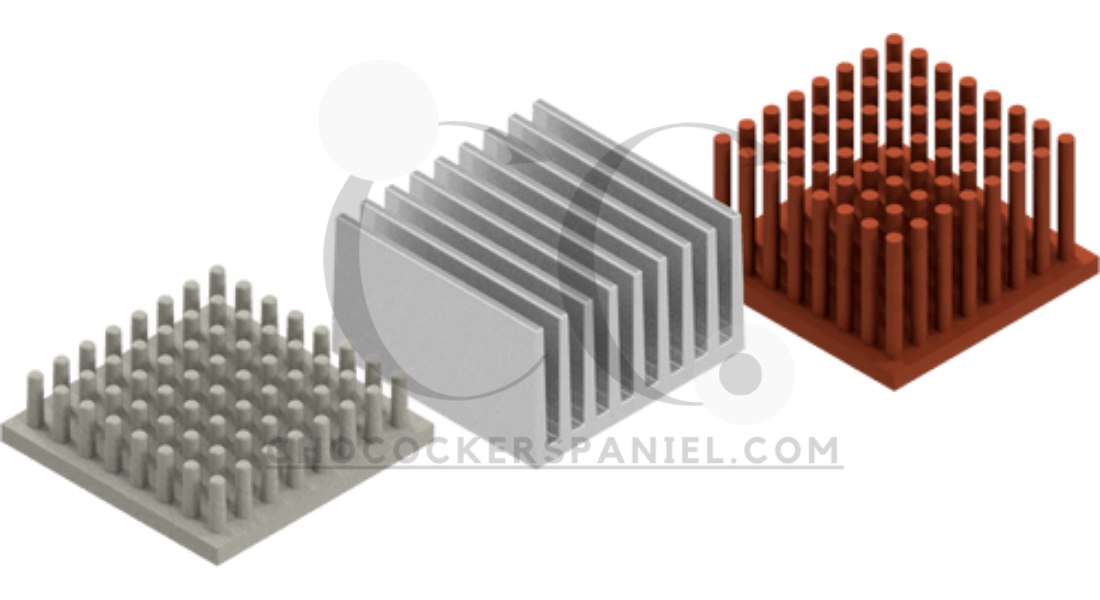
Effective thermal management is essential for maintaining the efficiency and longevity of electronic devices. Heat sink thermal solutions play a pivotal role in dissipating heat, ensuring components operate within safe temperature ranges. Explore the importance, types, and innovations surrounding these critical cooling components.
Heat Sink Thermal Solutions: Essential for Modern Electronics
As devices become more powerful, they generate higher levels of heat, necessitating efficient cooling solutions. Heat sinks transfer heat away from electronic components, preventing damage and improving performance. From CPUs to power amplifiers, they are integral to reliable operations.
Why Heat Sink Thermal Management Matters
Proper thermal management with heat sinks delivers several key benefits:
Enhanced Device Performance
By maintaining optimal temperatures, heat sinks ensure electronic components perform at their best without throttling or slowdowns.
Increased Longevity
Excessive heat accelerates wear and tear. Effective cooling extends the lifespan of components, reducing replacement costs.
Improved Energy Efficiency
Cooler components consume less power, making heat sinks an eco-friendly solution for energy savings.
Reduced Risk of Failures
Overheating can lead to malfunctions or permanent damage. Heat sinks mitigate these risks, ensuring reliability.
Versatility Across Applications
Heat sinks are used in diverse settings, from consumer electronics to industrial systems and renewable energy applications.
Types of Heat Sink Thermal Solutions
Different designs cater to varying cooling needs, offering flexibility and adaptability:
Passive Heat Sinks
Relying on natural convection, these are simple, cost-effective, and silent, making them ideal for low-power applications.
Active Heat Sinks
Equipped with fans or other mechanical components, active solutions enhance heat dissipation, suitable for high-performance systems.
Finned Heat Sinks
With extended surface areas, finned designs improve heat transfer efficiency, commonly used in CPUs and GPUs.
Liquid-Cooled Heat Sinks
For demanding applications, liquid-cooled systems provide superior performance by transferring heat through coolant channels.
Hybrid Systems
Combining passive and active elements, hybrid designs deliver a balance of efficiency and noise reduction.
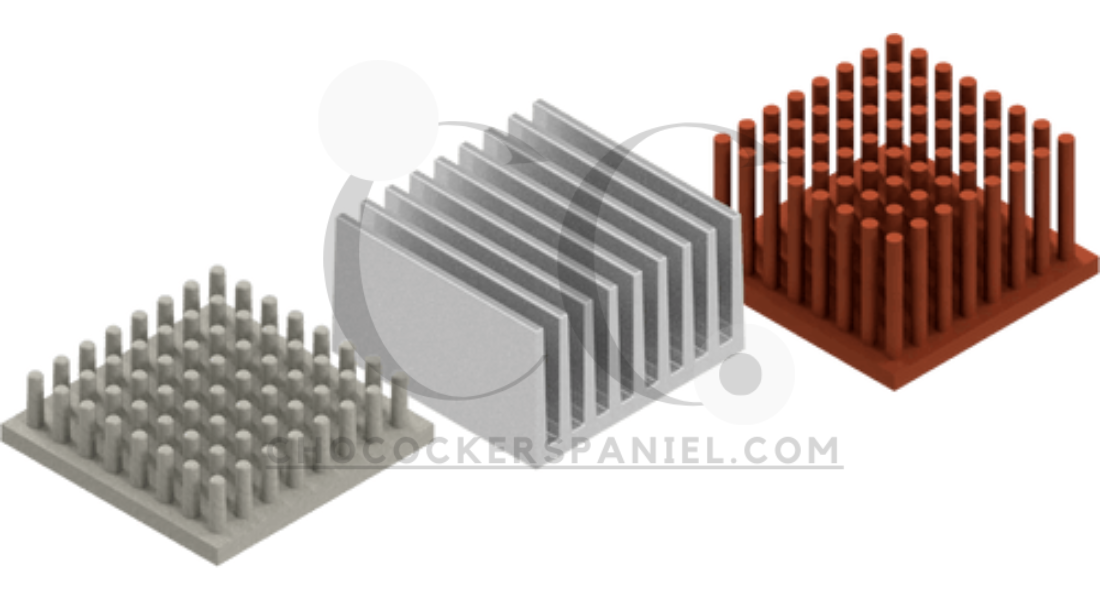
Key Features of Efficient Heat Sink Thermal Designs
Modern heat sinks incorporate advanced features to optimize cooling:
High Thermal Conductivity Materials
Aluminum and copper are popular choices due to their excellent thermal properties and lightweight nature.
Advanced Surface Designs
Fins, microchannels, and other innovations maximize surface area for improved heat dissipation.
Compact and Lightweight Structures
Modern designs prioritize space-saving and lightweight solutions without compromising efficiency.
Integration with Thermal Interfaces
Thermal paste, pads, or adhesives enhance conductivity between the heat sink and the component.
Customization for Specific Applications
Tailored designs cater to unique thermal challenges in automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications.
Applications of Heat Sink Thermal Solutions
The versatility of heat sinks makes them indispensable across numerous industries:
Computing and Electronics
In CPUs, GPUs, and power supplies, heat sinks ensure stable performance during intensive tasks.
Renewable Energy Systems
Solar inverters and wind turbine converters rely on efficient cooling to optimize energy conversion.
Automotive Electronics
Electric vehicles and modern cars use heat sinks in powertrain systems, battery packs, and infotainment devices.
Telecommunications
Base stations, routers, and other equipment require thermal management to handle continuous operation.
Industrial Machinery
Heat sinks in industrial equipment prevent overheating in motors, power converters, and automation systems.
Comparing Heat Sink Thermal Solutions
Each type of heat sink has unique advantages, making it essential to choose the right solution:
- Passive Heat Sinks: Silent and maintenance-free but limited in cooling capacity.
- Active Heat Sinks: Superior performance but require more power and maintenance.
- Finned Designs: High efficiency for compact spaces, ideal for computing.
- Liquid-Cooled Systems: Best for extreme performance but complex and expensive.
User Insights: Why Heat Sink Thermal Management Is Crucial
Professionals in computing, renewable energy, and manufacturing emphasize the importance of heat sinks in maintaining reliability and performance. Many note the reduced operational costs and enhanced efficiency achieved through effective thermal management. Whether for personal devices or industrial equipment, the value of heat sinks is universally acknowledged.
Tips for Maximizing Heat Sink Thermal Efficiency
To ensure optimal cooling performance, consider these best practices:
- Select the Right Material: Copper offers superior conductivity, while aluminum is lightweight and cost-effective.
- Optimize Airflow: Position heat sinks to maximize natural or forced airflow.
- Use Quality Thermal Interfaces: High-quality paste or pads improve heat transfer to the sink.
- Maintain Clean Surfaces: Dust and debris can impede performance; regular cleaning is essential.
- Monitor System Temperatures: Use sensors to track thermal performance and make adjustments as needed.
Future Trends in Heat Sink Thermal Technology
Innovations in material science and design are driving the evolution of heat sink solutions:
Graphene and Advanced Materials
Emerging materials like graphene promise unparalleled thermal conductivity, revolutionizing heat sink performance.
Miniaturization for Compact Devices
Smaller, more efficient heat sinks cater to the growing demand for compact consumer electronics.
Additive Manufacturing
3D printing enables highly customized heat sink designs for specific thermal challenges.
Smart Cooling Systems
AI and IoT integration allow for real-time monitoring and adaptive thermal management.
Sustainability
Eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes reduce environmental impact while maintaining efficiency.
Why Heat Sink Thermal Solutions Are a Smart Investment
Investing in effective thermal management not only improves device performance but also reduces operational costs and downtime. Heat sinks protect valuable components, ensuring long-term reliability and energy efficiency.
Conclusion: Empowering Electronics with Effective Cooling
Heat sink thermal solutions are more than just a necessity; they’re a cornerstone of modern engineering. By optimizing heat dissipation, these components ensure devices perform reliably and efficiently across diverse applications.
From personal electronics to industrial systems, heat sinks are essential for unlocking the full potential of modern technology. Embrace advanced thermal solutions to enhance performance, reduce risks, and achieve sustainable efficiency.
References
- Advancements in Thermal Management Materials: The role of graphene and other cutting-edge materials.
- Applications of Heat Sinks in Industry: Real-world examples from computing, automotive, and renewable energy sectors.
- Optimizing Cooling with Finned Designs: How surface area impacts thermal performance.
- Comparing Passive and Active Heat Sinks: Key differences and use case recommendations.
- Future Trends in Heat Sink Technology: Predictions for the next generation of cooling solutions.
Upgrade your devices and systems with heat sink thermal solutions that deliver efficiency, reliability, and sustainability. Whether for high-performance gaming, industrial machinery, or renewable energy, these cooling components are the backbone of advanced engineering.